Brain lymphoma
Brain lymphoma or central nervous system lymphoma (CNS) is an aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma in the same way as:
Diffuse lymphoma with large B cells;
The lymphoma of the mantle;
Burkitt's lymphoma;
Peripheral T-lymphoma;
Lymphoblastic lymphoma.
This lymphoma mainly concerns the elderly, but it remains relatively rare. However, there are risk factors associated with weakening of the immune system:
AIDS (most frequently);
Immunosuppressive therapy following organ transplantation;
Hereditary disorder.
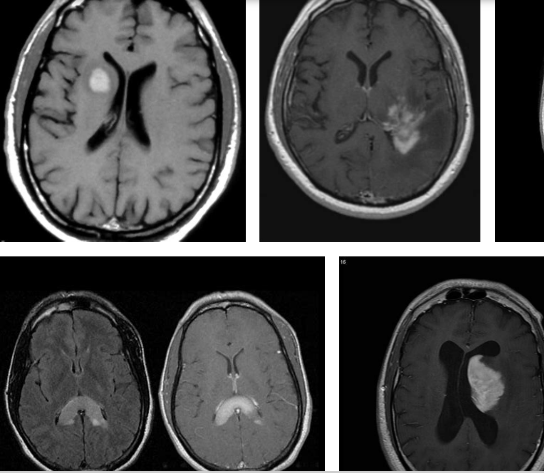
Localization of Brain lymphomas
Primitive lymphomas of the central nervous system are non-Hodgkin (NHL) lymphomas that appear in the brain or in the spinal cord. These are mostly B-type lymphomas. The most common forms of Cerveausont lymphoma are those that affect:
Areas around the cerebral ventricles (periventricular lymphoma);
Central grey nuclei;
The callus body (located between the cerebral hemispheres).
Nevertheless, it can also grow from:
Brain (CNS protective membranes);
Of the eye (cerebral eye lymphoma).
It is for this reason that an ophthalmological examination must always be carried out in patients with cerebral lymphoma, even in the absence of symptoms.
Brain lymphoma hardly ever spreads outside the CNS. On the other hand, a lymphoma or other type of cancer that appears elsewhere in the body can reach the brain (metastasis); In this case it is not a primary CNS lymphoma.
CNS Primary lymphoma Symptoms
The symptoms of CNS primary lymphoma are identical to those observed in other brain cancers. They are therefore very variable because they depend on the region concerned, knowing that several areas can be affected simultaneously. Some of the symptoms we can find include:
Headaches
Nausea and vomiting
Vision Disturbances
Speech disorders
Muscle weakness or difficulty coordinating gestures
Cognitive impairment (loss of memory, mental confusion, etc.).
In order to determine the presence of primary CNS lymphoma, the spinal fluid (CSF) puncture at the lumbar level is indispensable (in the absence of contraindications).
Prognosis and treatment of brain lymphomas
Brain lymphomas are usually bad prognosis. Indeed, on the one hand they are aggressive lymphomas, on the other hand they often cause relapses. The prognosis is particularly bleak at:
Persons over the age of 60;
People who are struggling to continue their daily activities
People who are infected with AIDS or who have a weakened immune system.
The treatment of primary central nervous system lymphoma is usually used in isolation or in combination with:
Corticosteroids for destroying cancer cells and reducing cerebral edema;
Specific chemotherapy (drugs that will be able to reach the brain, which is usually not the case) based on methotrexate and cytarabine at high doses; You can also go intravenously or intrathecal (directly into the CSF).
Complete brain radiation therapy, including in case of eye lymphoma.








0 komentar:
Posting Komentar